Mass Gainers vs. Whey Protein: Which is Right for You?
When it comes to achieving fitness goals, especially related to muscle gain, weight management, and body composition, supplements can play a pivotal role. Among the most popular and widely debated options are mass gainers and whey protein. Each supplement serves a different purpose, and understanding the distinction is key to making an informed decision. In this in-depth guide, we explore the fundamental differences, benefits, ideal use cases, and potential drawbacks of mass gainers and whey protein to help you decide which is better for your individual goals.

What is Whey Protein?
Whey protein is a high-quality protein derived from milk during the cheese-making process. It contains all nine essential amino acids, making it a complete protein. It is particularly known for its quick absorption rate and high concentration of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), which are essential for muscle repair and growth.
Types of Whey Protein
- Whey Protein Concentrate (WPC): Contains low levels of fat and carbohydrates. Protein content varies between 70% to 80%.
- Whey Protein Isolate (WPI): Further processed to remove fat and lactose. Protein content is usually over 90%.
- Whey Protein Hydrolysate (WPH): Predigested form of whey protein that allows faster absorption.
What are Mass Gainers?
Mass gainers are high-calorie supplements designed to help individuals gain weight and muscle mass. They are typically composed of a combination of protein, carbohydrates, and fats. The protein content is generally lower than whey protein per serving, but the caloric content is significantly higher.
Key Ingredients in Mass Gainers
- Complex Carbohydrates: Such as maltodextrin, oats, or sweet potato powder
- Protein: Usually a blend of whey protein, casein, and sometimes plant-based protein
- Healthy Fats: MCT oil, flaxseed, or sunflower oil
- Micronutrients: Vitamins and minerals to support overall health
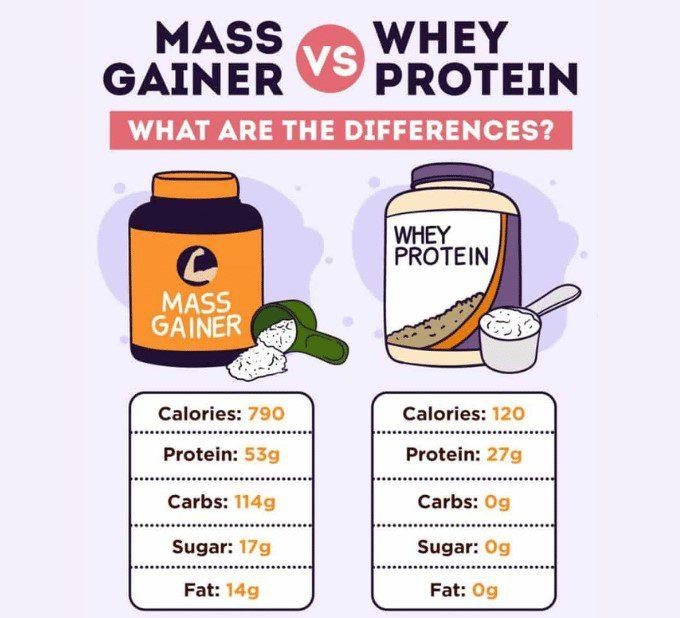
Key Differences Between Mass Gainers and Whey Protein
| Feature | Mass Gainers | Whey Protein |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Weight and muscle gain | Muscle repair and lean muscle growth |
| Calories per serving | High (600-1200) | Moderate (100-150) |
| Protein content | Moderate (20-50g) | High (20-30g) |
| Carb content | High (60-200g) | Low (1-5g) |
| Fat content | Moderate to high | Low |
| Ideal for | Hard gainers, ectomorphs | General fitness, athletes, bodybuilders |
Benefits of Whey Protein
1. Muscle Growth and Repair
Whey protein is rich in leucine, a key amino acid that stimulates muscle protein synthesis. It’s ideal for post-workout recovery and building lean muscle mass.
2. Weight Management
Due to its high protein content and low calorie count, whey protein helps with satiety and can be used in weight loss programs.
3. Fast Absorption
Its quick digestion makes it perfect for immediate post-exercise nutrition.
4. Immune Support
Whey protein contains immunoglobulins and lactoferrin, which may support immune function.

Benefits of Mass Gainers
1. Calorie-Dense Formula
Mass gainers provide a high number of calories in a single serving, helping individuals meet their daily caloric intake requirements easily.
2. Muscle Mass Increase
The combination of proteins and carbs promotes insulin release, which helps shuttle nutrients into muscle cells.
3. Time-Efficient Nutrition
Mass gainers are convenient for those with busy lifestyles who struggle to consume enough calories through whole foods.
4. Supports Recovery
The blend of macro- and micronutrients can help improve recovery post-workout.When Should You Use Whey Protein?
- Post-Workout: For fast muscle recovery
- Between Meals: To prevent muscle breakdown
- During Weight Loss: As a low-calorie meal supplement
- In High-Protein Diets: To meet daily protein requirements
When Should You Use Mass Gainers?
- If You’re a Hard Gainer: Struggle to gain weight despite eating large meals
- During Bulking Phase: To support muscle mass increase
- When Time is Limited: Fast, convenient calorie source
- In High-Calorie Diets: To fulfill daily caloric goals
Potential Drawbacks of Whey Protein
- Lactose Intolerance: May cause digestive issues in sensitive individuals
- Short-Term Fullness: Doesn’t provide lasting satiety due to low fat/carbs
- Over-Reliance: Should not replace whole food nutrition
Potential Drawbacks of Mass Gainers
- Excess Calories: Can lead to fat gain if not paired with exercise
- Sugar Content: Some mass gainers contain added sugars
- Digestive Issues: High calorie load can be hard on the stomach for some
Which One is Better for You?
The choice between mass gainers and whey protein depends on your specific goals, body type, and nutritional needs.
Choose Whey Protein If:
- Your goal is to build lean muscle
- You are aiming for fat loss or weight maintenance
- You need a high-quality protein source
- You’re on a high-protein, low-carb diet
Choose Mass Gainers If:
- You are underweight or a hard gainer
- You struggle to meet your daily calorie intake
- You are in a bulking phase and require high energy
- You have a high metabolism and need quick nutrition

Ideal Users of Whey Protein
Whey protein is commonly used by:
- Athletes
- Bodybuilders
- Fitness enthusiasts
- Individuals following a high-protein diet
It is also suitable for older adults who need additional protein to maintain muscle mass and strength.
Ideal Users of Mass Gainers
Mass gainers are best for:
- Ectomorphs (naturally thin individuals)
- Beginners who are underweight
- Individuals recovering from illness or surgery
- People with high-calorie needs (e.g., labor-intensive jobs)
Combining Whey Protein and Mass Gainers
In some cases, it may be beneficial to use both supplements strategically. For example, you can use whey protein post-workout and mass gainer shakes between meals or before bed to maximize muscle growth and recovery.
What to Look for in a Quality Supplement
For Whey Protein:
- Low in added sugars and artificial flavors
- High protein content (20g or more per serving)
- Third-party tested for quality
- Good mixability and taste
For Mass Gainers:
- Balanced macro ratio (protein to carbs)
- Low in refined sugars
- Contains digestive enzymes to aid absorption
- Includes essential vitamins and minerals
Conclusion
Mass gainers and whey protein both offer unique benefits, but their effectiveness depends on your individual fitness goals. If you aim to build lean muscle while keeping your calories in check, whey protein is a more efficient option. On the other hand, if gaining weight and muscle mass is your primary objective, mass gainers offer a calorie-dense solution that simplifies your nutrition plan.
Always consider your lifestyle, metabolism, workout intensity, and dietary needs when selecting a supplement. Whether you choose whey protein, mass gainers, or both, ensure it fits into a well-rounded diet and training program. For optimal results, consult with a fitness professional or a certified nutritionist.
By understanding the nuances of each supplement, you can make informed decisions that support your long-term health and fitness journey.